Table of Contents
How To Turn A 7th Chord Into A Rootless 9th Chord
This chord theory lesson focuses on how to transform a dominant 7 chord (drop 2, drop 3 and related inversions) into a rootless ninth chord by replacing the tonic (1) with the ninth (9).
This technique will help guitarists expand their harmonic knowledge and also explore their neck in more depth. This can be a useful trick when composing or for chord melody arrangements.
What’s A Dominant 7 Chord?
Dominant seventh chords have a very important role in jazz and blues music, they are the most versatile. Indeed, they accept a lot of extensions as 9, 11, 13 and also altered tones as b5, #9, b9, #11, b13.
Firs table, you need to know that dominant 7 chords are built on the basis of a major triad (R – 3 – 5). A minor seventh is added to this triad to get a dominant seventh chord, thus giving the interval formula R (root), major third (3), fifth (5) and minor seventh (b7). For example a C7 chord is made of C (R), E (3), G (5), Bb (b7).

What’s A Ninth Chord?
A ninth chord is seventh chord with a supplementary note, the ninth (9). There are three main types of ninth chords that are : Major ninth ( 1 – 3 – 5 – 7 – 9), minor ninth (1 – b3 – 5 – b7 – 9) and dominant ninth (1 – 3 – 5 – b7 – 9).
Even if the following technique works for any type of ninth chord, we will take the dominant 9 chord as example. As shown in the chart below, to create a dominant ninth chord from a dominant seventh chord, just add the ninth (D in the example).

What’s A Rootless Chord Voicing?
The answer is in the question. A rootless chord is simply a chord whose root as been removed.
How To Build A Rootless 9th Chord From A 7th Chord?
To build rootless dominant 9 chords, just remove the root of a dominant seventh chord and replace it by the 9th. Remember that it works for any type of seventh chord (minor 7 to rootless min9 and major 7 to rootless major 9 for example)
Rootless Dominant 9 Guitar Chord Shapes (drop 2)
Here are four dominant 9 guitar chord shapes built from four drop 2 dominant 7 voicings (1 root position and 3 inversions) with bass notes on low E string. R being the root note, 3 the major third, 5 the perfect fifth and b7 the minor seventh.
The root of the 7th chord is simply raised by a whole step to get the 9th of the dominant 9 chord.
This summary table show the interval formulas related to the next guitar neck diagrams.

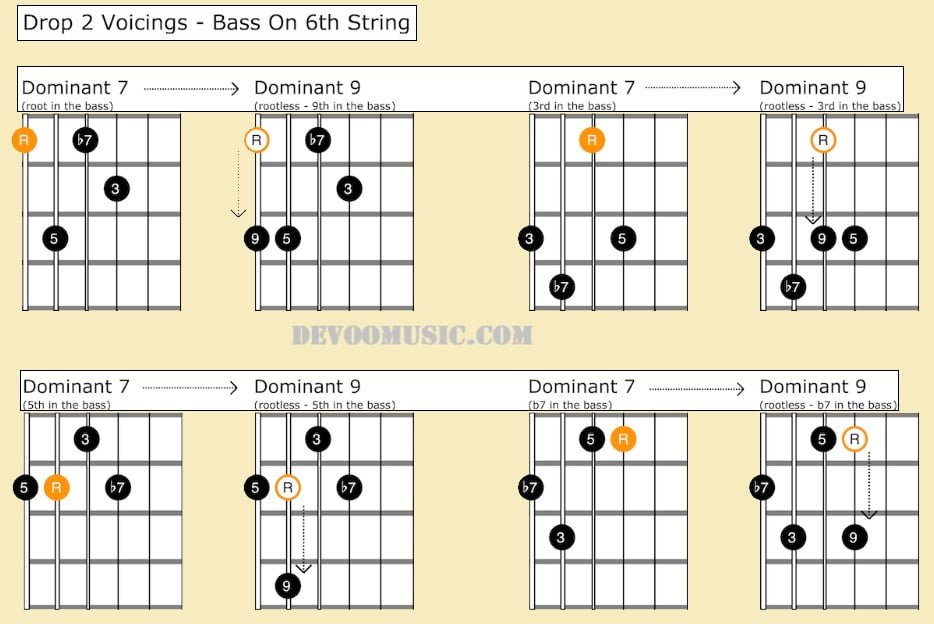
Here are four dominant 9 shapes with bass notes on the A string.

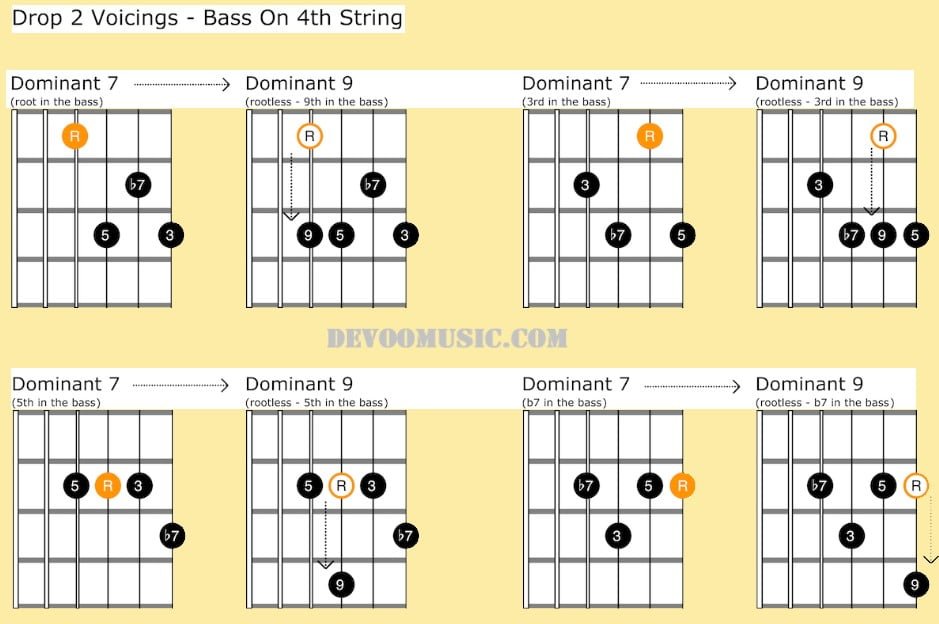
Regarding these next diagrams, the bass notes are on the D string.
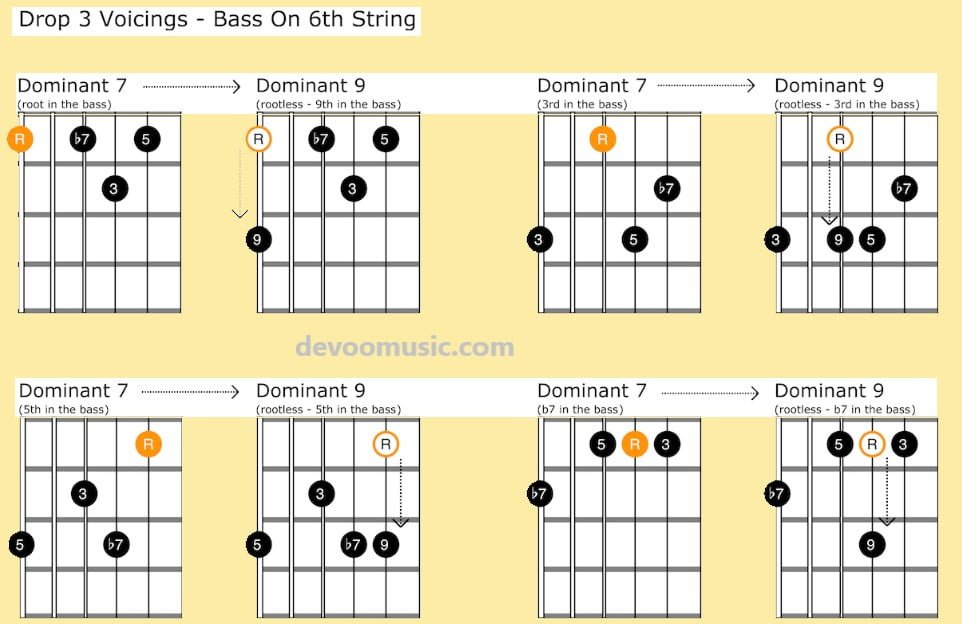
Rootless Dominant 9 Guitar Chord Shapes (drop 3)
Let’s tackle the dominant 9 chords based on the drop 3 dominant 7 shapes. You’ll find below a recapitulative chart and the related guitar chord shapes with bass notes on the low E string.

These last dominant chord shapes have bass notes on the A string.

Comparison With Half-diminished Chords
One interesting thing which can be useful for chord substitution is that rootless dominant 9 chords shapes are actually the same as half-diminished (m7b5).
For example you can see and hear that a m7b5 chord with root in the bass is the same form as rootless dominant 9 chord with major third (3) in the bass.
Here are eight shapes to illustrate this theory, which applies to any drop 2 or drop 3 half-diminished chord.

Comparison With minor 6 Chords
Rootless dominant 9th chord shapes can also be compared with minor 6 shapes. Let’s take the minor 6 shape with the root in the bass, you see that it is actually a rootless dom9 chord with 5th in the bass.
This applies to any m7b5 drop voicings. So try to make the conversion and find the positions on the guitar.

Thank You

More
25 Exotic Scales On Guitar – Charts, Easy Diagrams And Audio
This guitar lesson lists 25 exotic scales from different cultures…
Jazz Guitar Scale Easy Exercises – Shapes with the Melodic Minor Scale 2@22
earning and playing scales can be an important part of…
Tera Yaar Hoon Main Easy Guitar Chords 2@21
Tera Yaar Hoon Main [G] Tu jo rootha toh [C]…
Roke Na Ruke Naina Easy Guitar Chords – Badrinath Ki Dulhania 2022
(G) Tu jo nazron ke saamne (Em) kal hoga nahi…
Ludo: Aabaad Barbaad Easy Guitar Chords | Arijit Singh 2022
Ya to bar(G)baad kar do (D) Ya phir aa(C)baad kar…
Mixolydian blues Scale | Easy Guitar Shapes & licks 2022
The mixo-blues scale can be confusing because of its different…