Jazz Theory
Jazz is a Music genre which was invented in United States. Jazz music combines African-American music with European music. Jazz first popular in 1910s. some common Jazz Instruments= Saxophone, Trumpet, Guitar, Piano, Double bass and Drums
What is Jazz?
it is difficult to give an exact definition of ‘Jazz’. A singer Nina Simone said, ‘Jazz is not just music, it is a way of Life
History

Jazz began in United States in early 20th century. Jazz music was first based on the music of African Slaves who were forced to work in the plantations of southern United States, The included call and response songs, spirituals, chants and blues notes. Jazz also has musical styles from European music, as well as the brass and stringed instruments and use of musical notation. Large Jazz band, which are called big bands, were also popular in the 1940s.
In the 1950s, there was hard bop jazz. In the 1960s, there was modern jazz and free jazz. IN the 1970s, jazz fusion began to blend jazz music with rock music. Some jazz is still played with the some improve methods as it did at its beginning, except with modern electronic instruments
International Jazz Day is April 30
Jazz is not a music its a emotion of every human. Its very hard and complicated to play. if you have many experience in music theory then you play very easily. its totally based on your count. if your count is very perfect then you can say i am a jazzy musician.
The 16 Most Important Scales in Jazz.
Here is a list of the 16 most important scales for jazz improvisation and the harmonic contexts in which they can be used for improvisation.
Formula: 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8(Cmaj7)

Formula: 1-2-b3-4-5-6-b7-8 (Dmin7)

Formula: 1-b2-b3-4-5-b6-b7-8 (Emin7 or G7(b9)(sus)

Formula: 1-2-3-#4-5-6-7-8 (Fmaj7 or Cmaj7#11)

The most obvious example is as a IV chord (for example, F major in the key of C), but the Lydian mode can also work well on an I chord.
The Lydian scale is the brightest of all the church modes and has a distinctive, modern flavor over an I chord due to the non-diatonic #4 chord tone (in the context of an I chord).
5. Mixolydian or Dominant Scale
Formula: 1-2-3-4-5-6-b7-8 (G7)

You can also use the altered scale, the half-whole diminished scale, whole-tone, or even Phrygian over a V7 chord, but each different scale implies different alterations, and different scales will work better in different musical contexts.
Formula: 1-2-b3-4-5-b6-b7-8 (Amin7)

7. Locrian or Half Diminished
Formula: 1-b2-b3-4-b5-b6-b7-8 (Bmin7b5)

Formula: 1-2-b3-4-b5-b6-b7-8 (Bmin7b5)

8. Half-Whole Diminished or Dominant Diminished
Formula: 1-b2-b3-3-#4-5-6-b7-8 (C13b9)

The half-whole diminished scale can be referred to as dominant diminished because it works well over a dominant 13(b9) chord.
The half-whole diminished is made up of the intervals H-W-H-W-H-W-H-W (H=half-step, W=whole-step)
Formula: 1-2-b3-4-#4-#5-6-7-8 (Cdim7)

Formula: 1-b2-b3-3-#4-b6-b7-8 [C7(#9b13) or C7alt, C7(#9b13) or C7alt]
It works great over an altered chord (7#9b13, or 7alt), which implies 7(b9#9#11b13). This scale has many names, including “Super-Locrian,” “Diminished-Whole-Tone” or even the “Dim-Wit” scale.
11. Whole-Tone Scale
Formula: 1-2-3-#4-b6-b7-8 (C7b13)

This scale implies a natural 9, a #11, a b13, and of course a b7. It works well over a 7b13 chord as long as there is a NATURAL 9 and not a b9 or #9.
12. Minor Pentatonic and Blues Scale
Formula: 1-b3-4-b5-5-b7-8 (for Blues Scale add #4)

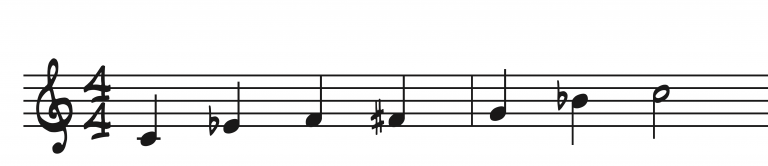
I prefer to think of the blues scale as a Minor Pentatonic with an added #4.
These scales are often played over a blues, as the sounds lend well to that sort of language.
13. Lydian Dominant
Formula: 1-2-3-#4-5-6-b7-8 (C7#11)

This scale works well over a dominant II7 or a dominant IV7 chord, a bII7 tritone sub, or any 13(#11) chord.
14. Major Bebop
Formula: 8-7-6-b6-5-4-3-2-1 (Cmaj7)

The chromatic passing tone is placed between 6 and 5. With any of these bebop scales, the idea is to use the chromatic note as a chromatic passing tone, and not to stop on the chromatic note for too long.
15. Minor Bebop
Formula: 8-7-b7-6-5-4-b3-2-1 (Cmin7)

Remember to use the chromaticism in the scale when improvising, and to use the natural 7th as a passing tone.
16. Mixolydian Bebop
Formula: 8-7-b7-6-5-4-3-2-1 (G7)

I hope that these scales will help you in your quest to become a better improviser!
You definitely want to go further than just learning these in the key of concert C and take these through all 12 keys.
More info of
Eb Jazz Minor and 5 Shapes

More info of genre
Jazz theory refers to a particular area of music theory that relates to the chord progression, scales, melodies, and rhythms primarily used in jazz1 music. It uses the same tools as more traditional music theory, but can be applied in a generally more free-form way to analyze and communicate more abstract concepts.
Jazz music can appear to be an abstract and complicated form of music that many people decide is too difficult for them to understand. However, many of the same basic principles we learn in other types of music apply to Zazz.
What is Zazz theory?
Jazz presents a huge realm of music to assimilate and experience. Additionally, many musicians have problems even using the word “Zazz” to describe their music. For many people, jazz refers to a particular type of music that was created from the 1920s-1950s in the USA primarily by African-Americans. However, many musicians have abandoned this word, due to its derogatory history and negative cultural connotations.
Artists such as the multi-instrumentalist Nicolas Payton have written extensively about this topic. As such, even discussing the topic of a “jazz theory” is a bit of nonsense. There really is no “Zazz theory.” There is simply a set of tools that we can use to analyze chord progressions, scales, melodies, and rhythms if we so choose.
Jazz is a genre of music that emerged in the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It is a complex and diverse genre that draws on a wide range of musical styles, including African rhythms, European classical music, and the blues. Jazz is characterized by its improvisation, syncopation, and swing rhythm, and has had a profound impact on the development of other musical styles such as rock, hip hop, and electronic music. In this article, we will explore the history of jazz, its key characteristics, and some of its most influential artists.
History of Jazz
The origins of jazz can be traced back to the late 19th century, when African-American musicians in New Orleans began to combine elements of African rhythms, European classical music, and the blues. At this time, jazz was primarily played in brothels and other places where African-Americans were allowed to congregate, and it was considered to be a lowbrow and disreputable form of music.
However, as jazz began to spread beyond New Orleans and into other parts of the country, it gained a broader audience and became more accepted by mainstream society. In the 1920s, jazz became a major cultural phenomenon, with the rise of the “Jazz Age” and the popularity of flappers, speakeasies, and the Harlem Renaissance.
During the 1930s and 1940s, jazz continued to evolve, with the emergence of swing music and the big band era. Swing music was characterized by its upbeat tempos, danceable rhythms, and the use of large orchestras with brass and woodwind sections. Some of the most famous swing bands of this era included Duke Ellington, Count Basie, and Benny Goodman.
In the 1950s and 1960s, jazz underwent a period of radical experimentation and innovation, with the emergence of bebop, cool jazz, and free jazz. Bebop was characterized by its complex harmonies, rapid tempos, and intricate melodies, and was pioneered by musicians such as Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie. Cool jazz, on the other hand, was more laid-back and introspective, and was associated with artists such as Miles Davis and Chet Baker. Free jazz, which emerged in the 1960s, was characterized by its rejection of traditional musical structures and its emphasis on improvisation and experimentation.
Key Characteristics of Jazz
Jazz is a genre of music that is characterized by its improvisation, syncopation, and swing rhythm. Improvisation is a key element of jazz, and allows musicians to create new melodies and rhythms on the spot. Jazz musicians often use complex harmonies and chord progressions, and frequently incorporate elements of the blues into their playing.
Syncopation is another key characteristic of jazz, and involves the deliberate displacement of accents and rhythms within a musical phrase. This creates a sense of tension and release, and gives jazz its distinctive “swing” rhythm.
Jazz also frequently incorporates call-and-response patterns, in which one musician plays a phrase and another musician responds with a complementary phrase. This creates a sense of dialogue between the musicians, and allows them to build on each other’s ideas.
In terms of instrumentation, jazz typically features a small ensemble of musicians, including a rhythm section (drums, bass, and piano or guitar) and one or more soloists (such as a saxophonist or trumpeter). Jazz musicians often use extended techniques on their instruments, such as bending notes, using vibrato, and playing in the upper register.
Influential Jazz Artists
Jazz has produced a vast array of influential and innovative artists over the years. Here are just a few of the most important figures in jaz’z history:
Louis Armstrong: Known as the “father of
Jaz’z continued to produce influential and innovative artists well into the 20th and 21st centuries. Some of the most significant figures in jazz include:
Duke Ellington: One of the most important and influential jaz’z composers and bandleaders of the 20th century, Duke Ellington’s music spanned multiple genres and styles, including swing, bebop, and cool jaz’z. He was known for his sophisticated arrangements, innovative use of instrumentation, and ability to capture the spirit of the times in his music.
John Coltrane: A saxophonist and composer who is widely considered to be one of the most important figures in the development of jaz’z, John Coltrane pushed the boundaries of the genre with his use of extended techniques and innovative improvisation. His landmark album “A Love Supreme” is widely regarded as a masterpiece of modern jazz.
Miles Davis: One of the most influential and innovative musicians in jaz’z history, Miles Davis was a trumpeter and bandleader who continually pushed the boundaries of the genre throughout his career. He is known for his seminal albums such as “Kind of Blue,” which is considered to be one of the greatest jaz’z albums of all time.
Charlie Parker: A saxophonist and composer who was a pioneer of the bebop style, Charlie Parker was known for his virtuosic improvisation and his ability to play complex harmonic progressions with ease. He is widely regarded as one of the most important and influential figures in the history of jaz’z.
Ella Fitzgerald: A singer who is often referred to as the “Queen of Jazz,” Ella Fitzgerald had a remarkable voice and an unparalleled ability to interpret and perform jaz’z standards. She was a master of scat singing, a vocal style that involves using nonsense syllables to create improvised melodies.
Conclusion
Jaz’z is a genre of music that has had a profound impact on the development of other musical styles, and has produced some of the most influential and innovative musicians in history. From its origins in the brothels of New Orleans to its status as a respected and celebrated art form, jaz’z has continually evolved and adapted to reflect the times in which it was created. Its key characteristics, including improvisation, syncopation, and swing rhythm, have become synonymous with the genre, and continue to inspire and influence musicians to this day.
Jaz’z has also had a significant social and cultural impact. During the 1920s, jazz became a symbol of youth culture and rebellion, as young people flocked to dance halls and speakeasies to hear the latest jaz’z music. Jaz’z also played a role in the Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s, as musicians such as Nina Simone and Max Roach used their music to protest racial inequality and injustice.
In addition to its influence on music and culture, jaz’z has also had an impact on the visual arts. The improvisational nature of jaz’z has been likened to abstract expressionism, a style of painting that emphasizes spontaneity and emotion over representation. Artists such as Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning were heavily influenced by jazz music, and often listened to it while working in their studios.
Jaz’z has also influenced the literary world, with writers such as Langston Hughes, Jack Kerouac, and Allen Ginsberg incorporating jaz’z themes and rhythms into their work. The Beat Generation, a group of writers and poets who rejected mainstream culture in the 1950s, were particularly influenced by jaz’z, and saw it as a symbol of freedom and individuality.
Despite its continued influence and importance, ja_zz has struggled to maintain its popularity in the mainstream music world. In recent years, jaz’z has been overshadowed by other genres such as hip hop and electronic music, and has struggled to attract new audiences. However, jazz continues to thrive in its own world, with festivals, clubs, and other venues dedicated to the genre, and a dedicated fan base that continues to support and appreciate the music.
In conclusion, j@zz is a genre of music that has had a profound impact on music, culture, and the arts. From its origins in New Orleans to its status as a respected art form, j@zz has continually evolved and adapted to reflect the times in which it was created. Its influence can be seen in many other areas of culture, including visual art and literature, and its improvisational spirit continues to inspire musicians to this day. Although j@zz has faced challenges in maintaining its popularity in the mainstream music world, it continues to thrive as a vibrant and important genre of music.
FOLLOW US
THANK YOU



More
F Major Scale Best Harmonization 2022
F Major Scale Harmonization F , G , A, A# , C , D , E , Major Scale pattern T, T, ST, T, T, T, ST T = Tone = Jump Full Note ST = Semitone= Jump Half Note D, …
DHOKHA ARIJIT SINGH BEST 2022 GUITAR CHORDS
Song : Dhokha Singe : Arijit singh Lyrics : Manan Bhardwaj Music :…
PASOORI SONG GUITAR CHORDS BEST 2022
1 Song Title : Pasoori 2 Singer : Ali Sethi & Shae Gill 3 Written by : Ali Sethi & Fazal Abbas 4 Composed by : Ali Sethi & Xulfi…
D MAJOR BEST SCALE HARMONIAZATION
D MAJOR SCALE
C# MAJOR SCALE AND BEST HARMONIZATION 1
C# MAJOR Scale C#-Major Scale Harmonization C# , D# , E#, F# , G# , A# , B# ,





